IS THE EV CHARGING INFRASTRUCTURE READY FOR THE ELECTRIC REVOLUTION?
The world is shifting towards a cleaner, electrified future. With rising environmental concerns, fluctuating fuel prices, and advancements in battery technology, electric vehicles are no longer a niche segment—they are the future of mobility. Countries like China, the US, and Europe have already made significant progress in building EV-friendly ecosystems, but where does India stand in this transition?
India is witnessing a rapid surge in EV adoption, especially in the two-wheeler (2W) and three-wheeler (3W) segments. However, the country’s charging infrastructure remains a major challenge, with a stark gap between EV sales and the number of public charging stations. Without a strong and widespread charging network, large-scale EV adoption will remain a distant dream.
Can India catch up with global EV leaders, or will inadequate charging infrastructure slow down its electrification journey? Let’s dive in.
Understanding EV Chargers
How Do EV Chargers Work?
Electric vehicle (EV) chargers’ function by transferring electrical energy from a power source to an EV’s battery. The efficiency and speed of this process depend on the type of charger and the power supply available. Broadly, EV chargers operate on either Alternating Current (AC) or Direct Current (DC).
AC vs. DC Charging: What’s the Difference?
- AC charging supplies power in alternating current, which must be converted to DC by the car’s onboard charger before it can be stored in the battery. This makes AC charging slower but more widely accessible.
- DC fast charging bypasses the onboard charger and directly feeds direct current into the battery. This enables faster charging speeds but requires a more powerful electrical supply.
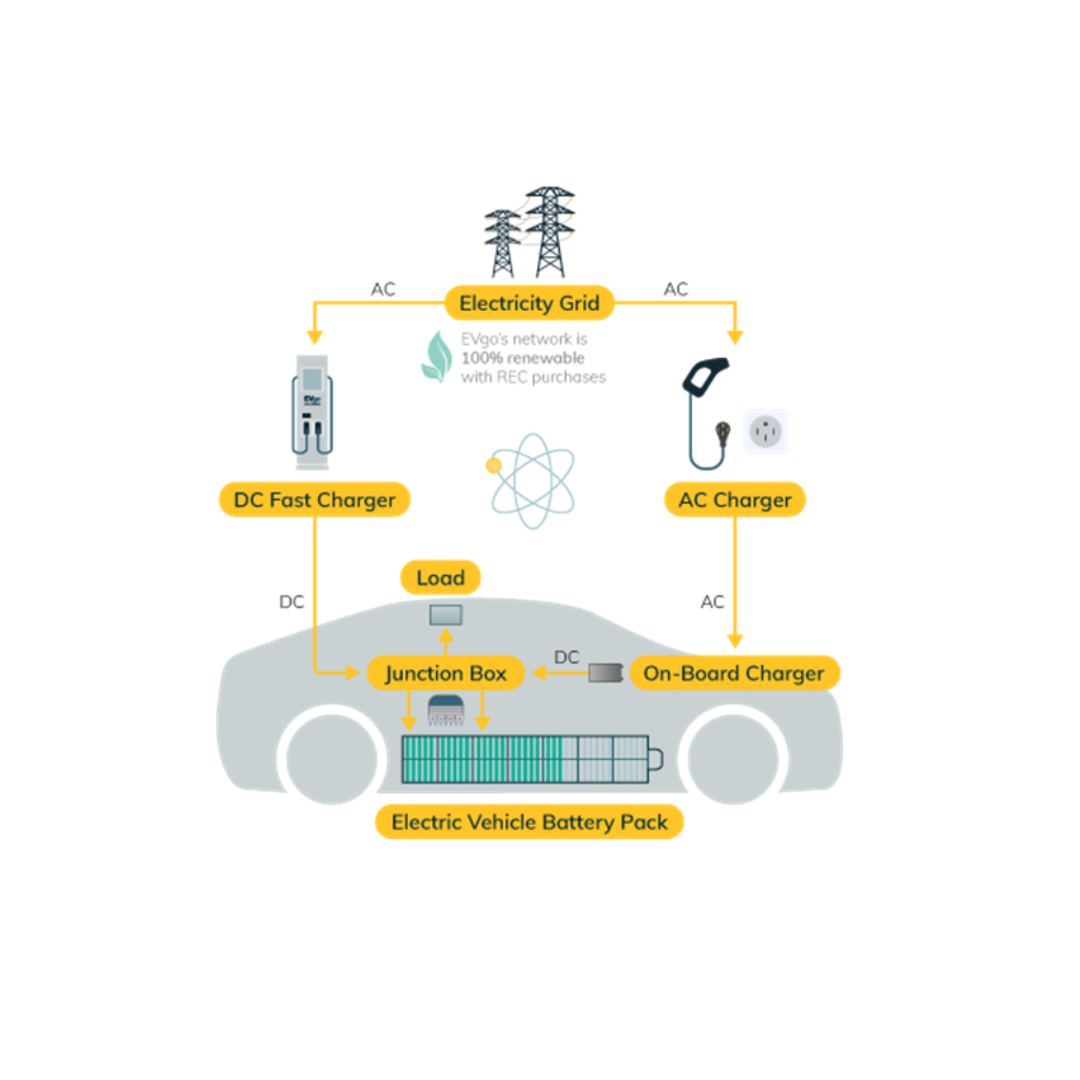
Levels of EV Charging: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3
EV chargers are categorized into three levels based on their voltage, power output, and charging speed:
| PARAMETERS | LEVEL 1 (AC) | LEVEL 2 (AC) | LEVEL 3 (DC) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | 240 | 380-400 | 200-1000 |
| Power (kW) | 1 to 3.3 kW | 3.3 to 22 kW | Up to 400 kW |
| Type of Vehicle | 4W, 3W, 2W | 4W, 3W, 2W | 4W |
LEV AC Chargers – Charging Sockets or Chargers?

With the increasing popularity of Light Electric Vehicles (LEVs)—such as e-scooters, electric motorcycles, and smaller EVs—there has been a growing demand for LEV (3.3kW) AC chargers. However, it is essential to clarify a common misconception:
LEV AC chargers are not traditional chargers but rather charging sockets.
Unlike standard EV chargers, LEV AC chargers do not have charging guns to directly plug into an EV. Instead, they serve as power outlets to which a compatible external charger must be connected. This means that many of the so-called “LEV AC chargers” being claimed by manufacturers are simply LEV AC 3.3 kW charging sockets rather than standalone chargers.
Chargers for 2W, 3W, and 4W EVs :
It is important to understand that chargers for cars, buses, and trucks differ significantly from those used for electric two-wheelers and auto-rickshaws. The former typically follow CCS or CHAdeMO standards and are designed for high-voltage batteries (above 100V). In contrast, EVs like scooters, bikes, and auto-rickshaws operate on lower-voltage batteries (below 100V) and use connectors such as Type 6, Type 7, Chogori, or LEV AC. These are entirely distinct standards optimized for their respective vehicle categories.
2W/3W EV Chargers
Two-wheeler (2W) and three-wheeler (3W) electric vehicles rely on different types of connectors and chargers, designed for smaller battery capacities and efficient power transfer.
The common charger types include:
- Type 7 – Common in e-scooters and small electric bikes.
- Type 6 – Used in compact urban electric vehicles.
- SB-50 – A versatile connector for small commercial EVs.
- SB-75x – Typically found in mid-range electric auto-rickshaws.
- Chogori – An emerging standard for robust electric two- and three-wheelers.
4W EV Chargers
Four-wheelers (4W) require higher-capacity chargers, available in AC and DC configurations, depending on vehicle requirements.
The most widely used connectors are:
- CCS2 – A popular global standard supporting both AC and DC fast charging.
- GB/T – The Chinese standard widely used in electric cars and buses.
- Type 2 – A commonly used AC charging connector in Europe and India.
- CHAdeMO – A Japanese fast-charging standard, known for high efficiency.
- NAAC (North American Automotive Charging) – The evolving standard for North America.
- NACS (North American Charging Standard) – Developed by Tesla and now being adopted by various manufacturers.

Charging Standards in India – Can Multiple Standards Be a Standard?
One of the most pressing challenges for India’s EV ecosystem is the lack of a uniform national charging standard. The country currently supports a range of charging interfaces—CCS2, CHAdeMO, GB/T, Type 2, and others—each with their own protocols, connector types, and power ratings. This leads to a fragmented charging infrastructure, creating challenges for both EV users and charge point operators.
Why Is This a Dilemma?
- Interoperability Issues: EV users may find themselves unable to charge their vehicles at certain stations due to incompatible connectors.
- Higher Costs: Charging station operators must install multiple types of chargers to support different standards, leading to higher capital costs.
- Slower Network Expansion: The lack of a unified standard slows down planning and deployment of charging infrastructure across cities and highways.
Global Best Practices
Countries like China and the EU have mandated national or regional charging standards (e.g., GB/T in China and CCS2 in Europe), streamlining infrastructure rollout. India, in contrast, continues to support multiple charging protocols in a bid to accommodate various OEMs and use cases.
Global CHARGING Infrastructure
Electric vehicle adoption has gained unprecedented momentum globally. In 2024 alone, EV sales crossed 16 million units, setting new records across major automotive markets. Governments worldwide are ramping up incentives, and private players are aggressively investing in charging infrastructure, particularly fast-charging networks in urban regions.
Public Charging Infrastructure: Uneven but Expanding
Globally, there are now over 3.9 million public charging points (as of 2023). However, their distribution is far from uniform:
- China leads by a significant margin, boasting 2.7 million public chargers, supported by state-driven policies and infrastructure mandates.
- Europe is catching up, driven by stringent emission regulations and climate targets.
- The United States is investing heavily through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law, but lags in rural accessibility.
Despite growth, a major bottleneck remains: the cost and complexity of installing charging stations, particularly in non-urban and developing regions. Fast-charging networks are crucial for long-distance travel and fleet operations, while home and workplace charging remain convenient but limited to urban consumers.
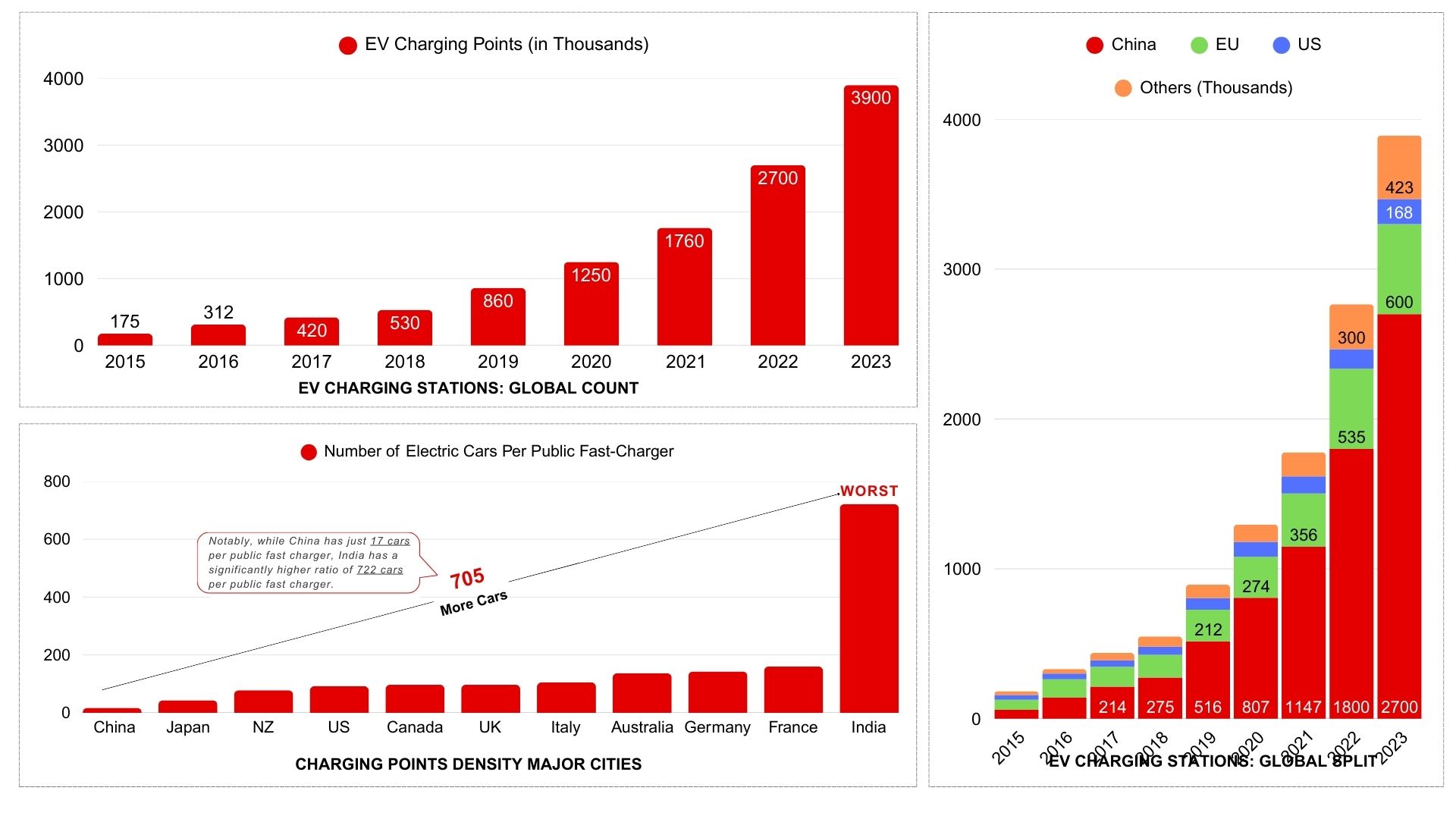
How Many Charging Stations Are There in India, Really?
According to the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), as of October 2024, India had 12,146 public EV charging stations catering to approximately 2.4 million EVs. But this figure, while official, may not represent the full picture.

A Gap Between Reported and Real
While government sources report around 12,000 stations, private companies claim significantly larger footprints:
- Statiq: Over 7,000 charging stations across India
- Bolt.Earth: Claims to operate 36,000+ charging points, positioning itself as India’s largest EV charging network
- ChargeZone: Over 1,500+ charging stations, branding itself as India’s fastest-growing network
- IOCL: States to have commissioned more than 10,000 EV charging stations across India.
This discrepancy raises a critical question: What is the actual number of operational EV charging stations in India?
Challenges in Estimating the Real Number
- Non-operational Chargers: A large portion of listed chargers are often non-functional. Reasons range from broken connectors or guns, power supply issues, or software failures. A survey by Massive Mobility in Delhi-NCR found that out of 2,200 listed chargers, only about 250 were operational — a shocking gap between claim and reality.
- Socket vs. Charger Confusion: Many claimed “chargers” are actually LEV AC 3.3kW sockets, not chargers with guns. These are basic power outlets designed for light electric vehicles, not true charging stations as users expect.
- Lack of Standardized Reporting: There is no unified, transparent system for tracking real-time operational status of chargers, making it nearly impossible to know how many are actually usable at any given time.
Why It Matters
This ambiguity affects consumer trust and hinders strategic planning for infrastructure deployment. Without accurate and standardized data, India risks overestimating its preparedness for EV adoption.
India vs. China
Both India and China are emerging as key players in the global EV ecosystem, but their approaches to EV infrastructure development differ significantly:
China’s Aggressive Push
China has rapidly expanded its EV charging network, with over 3.2 million public charging stations, government-backed policies, and leading battery technologies. Their focus on high-speed charging and urban-centric networks has helped drive EV adoption at scale.
India’s Gradual Approach
While India is making progress with policies like the FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) scheme, its infrastructure rollout is slower. The country has only about 12,000 public charging stations, and challenges like limited grid capacity, high land costs, and a fragmented market continue to slow expansion. However, the increasing push from the private sector and strategic partnerships may help India bridge the gap in the coming years.
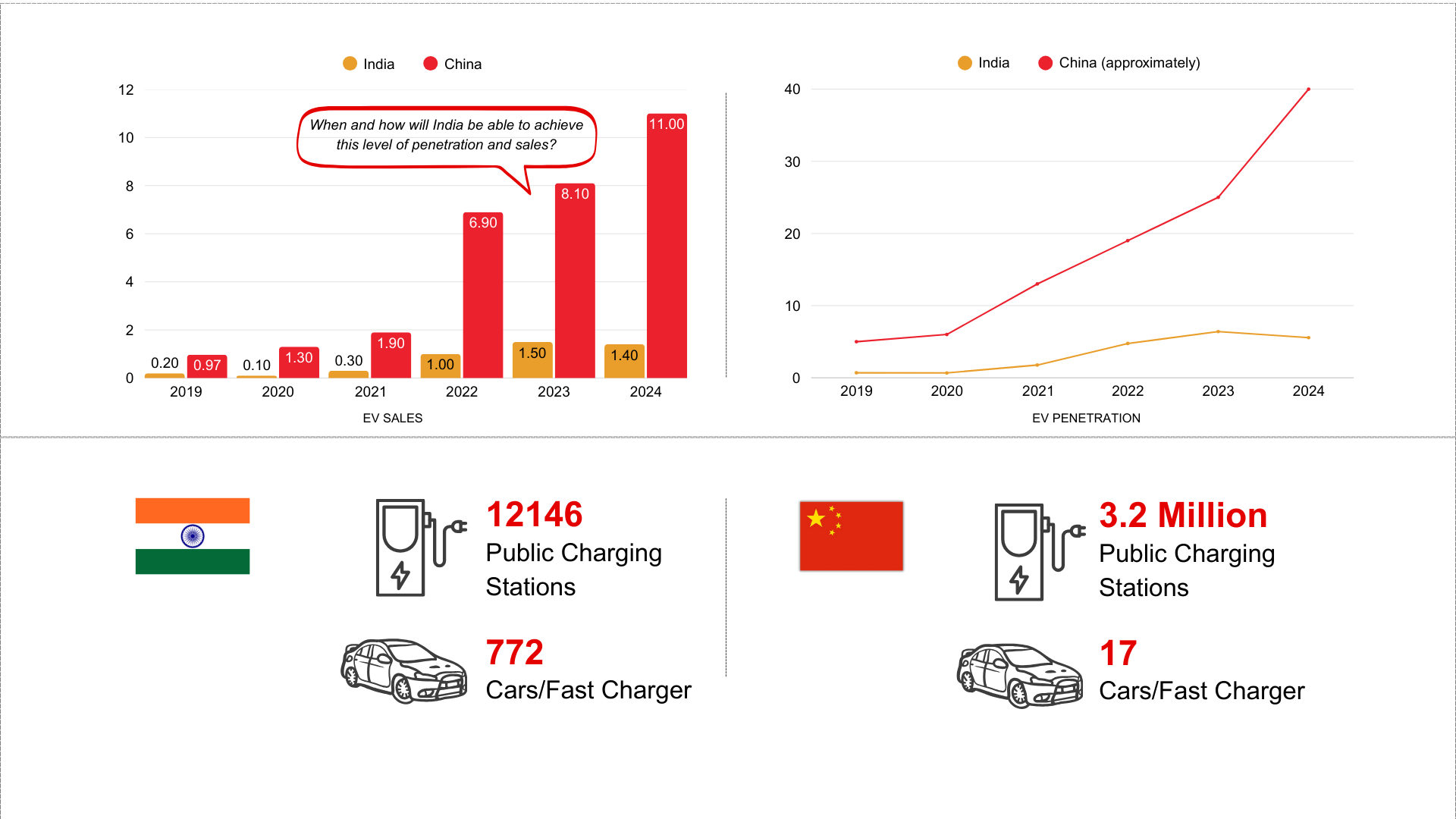
India’s EV journey is gaining significant traction, especially in recent years. As of October 2024, EV sales reached a milestone of 1,907,923 units, reflecting the nation’s growing appetite for cleaner mobility solutions. This surge is supported by policy incentives, state-level adoption, and increased consumer awareness.
Growing EV Sales in India
Monthly Sales Snapshot (Nov 2023 – Oct 2024)
- November 2023: 154,152 units
- March 2024 (Peak): 213,063 units
- April 2024 (Dip): 115,898 units
- October 2024 (Record High): 217,716 units
Together, 2W and 3W vehicles dominate, accounting for over 94% of India’s EV market, thanks to affordability and widespread commercial use.
India’s EV penetration has also reached 7.71% in 2024, a sharp rise from 6.47% in 2023.
Investment Trends
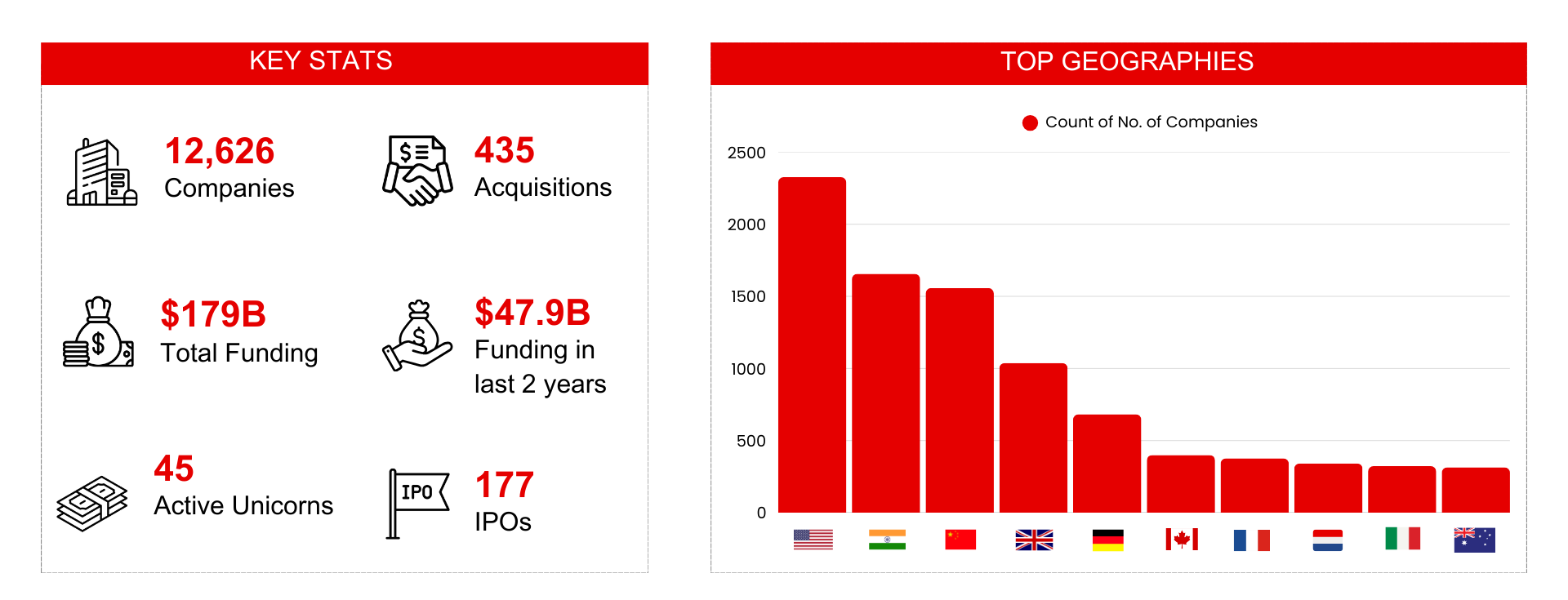
The EV charging sector is attracting significant investments from both public and private players. Global investments in EV infrastructure have surged, with over $179 billion allocated to charging expansion in the past years. Governments are offering subsidies, tax breaks, and grants to encourage infrastructure expansion, while private companies are focusing on innovative business models like subscription-based charging and pay-per-use networks.
Venture capitalists and automakers are also betting big on battery technology advancements, grid integration solutions, and charging-as-a-service models to ensure the sector’s profitability and long-term sustainability.
Policy Framework: What’s Driving EV Charging Expansion?
India’s electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem has undergone a remarkable policy evolution, with government interventions shaping the growth of EV infrastructure. Several key policies have played a crucial role in this expansion:
Key EV Policy Milestones
- Alternate Fuel for Surface Transportation Program (1998) – Early-stage initiative to promote alternative fuels.
- National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (2013) – Laid the foundation for EV growth, focusing on demand incentives and infrastructure development.
- FAME-I Scheme (2015-2019) – Introduced subsidies to reduce the cost of EVs and promote early adoption.
- FAME-II Scheme (2019-present) – Expanded incentives, particularly for two-wheelers, public transport, and charging infrastructure.
- Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme (2020) – Encouraged domestic manufacturing of EV components and batteries.
- Electric Mobility Promotion Scheme (2024) – Aimed at bridging the transition from FAME-II, focusing on key segments like e-2Ws and e-3Ws.
- PM Electric Drive Revolution in Innovative Vehicle Enhancement (PM E-Drive) – Expected to accelerate domestic production and infrastructure growth.
Subsidies to DISCOMs for EV Charging Expansion
One of the key challenges in expanding charging infrastructure is high electricity costs and grid integration.
To address this, the government is considering subsidies to DISCOMs (power distribution companies) to enable:
- Affordable electricity pricing for charging station operators.
- Grid enhancements to support fast-charging networks.
- Incentives for renewable energy-powered charging hubs.
With these measures, India aims to accelerate EV adoption by ensuring a robust, cost-effective, and widely accessible charging network.
The Road Ahead for EV Charging in India
India’s EV charging landscape is at a pivotal juncture. While significant strides have been made, critical challenges remain.
- To ensure sustainable growth, the country must focus on:
- Expanding public charging infrastructure, especially in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
- Standardizing charging protocols to reduce market confusion.
- Enhancing the operational reliability of existing charging stations.
- Boosting private sector participation through attractive investment incentives.
- Scaling up renewable energy-powered charging stations to make EV adoption more sustainable.
If these challenges are addressed efficiently, India has the potential to become a global leader in EV infrastructure development, supporting the transition toward a cleaner and more sustainable mobility future.
Download the Full Report
This report delves deeper into India’s EV infrastructure growth, policy landscape, investment outlook, and future challenges. Get the complete insights by downloading the full report now!
ABOUT STATE OF EV CHARGING

The “State of EV Charging” panel discussion was organized by the Massive Earth Foundation under its CLIMATE 101 program and sponsored by Climate Angels Fund and Massive Mobility Private Limited. The event brought together industry leaders, policymakers, and stakeholders to discuss the current EV charging landscape in India. The session delved into the sector’s challenges and opportunities, offering insights into the rapid growth of charging infrastructure and the way forward.
The panelists laid weight upon key trends in the EV landscape, including the dominance of 2-wheelers and 3-wheelers in adoption and the low utilization rates of public charging stations due to supply-demand mismatches. The panel also highlighted the critical role of policy support, grid capacity planning, and market-driven growth in shaping a sustainable EV charging ecosystem.
This engaging discussion offered valuable perspectives on how to address fragmentation and marked the release of State of EV Charging Report by Climate Angels Fund.
Agenda of the Report: State of EV Charging
E-Mobility Investments and Sales Trends
1
In-depth analysis of electric mobility investments and EV sales, both globally and in India. Highlighting the growing commitment to EV adoption, the role of investments in driving innovation, and the market dynamics shaping EV sales across different regions.
Current State of EV Charging Infrastructure
3
Exploring the development of EV charging networks globally and in India, the report examines the progress, challenges, and opportunities in expanding infrastructure. It delves into utilization rates, supply-demand mismatches, and regional differences in deployment. The section also highlights the rapid growth in charging infrastructure over recent years, the fragmentation caused by multiple operators, and the steps needed to ensure a more unified and accessible charging ecosystem.
Policy Framework and Regional Insights
2
A segment analyzes the role of national and state-specific policies in accelerating EV adoption and charging infrastructure development in India. It offers a detailed overview of policy incentives, subsidies, and regulatory frameworks that support growth. Additionally, it evaluates how these policies vary across states, highlighting their impact on infrastructure expansion and market penetration.
Key Stakeholder Takeaways
4
Finally, provides an overview of notable companies leading the EV charging landscape and concludes with actionable insights for stakeholders. It outlines strategies for businesses, policymakers, and investors to navigate and thrive in the evolving EV ecosystem.
Technological Innovations in EV Charging
5
Focused on advancements in charging technologies, the report delves into new innovations that are shaping the future of EV charging. It highlights emerging trends such as wireless charging, and vehicle-to-grid technology. The report also sheds light on the role of Charging Management Systems in optimizing the charging process, ensuring energy efficiency, and improving user experience. Additionally, it puts a spotlight on notable startups and companies driving innovation in the sector, offering insights into their contributions to making EV charging more efficient, sustainable, and accessible.
PANELISTS

Priyans Murarka
Founder, ExpWithEVs.in

Ameen Khan
Founder & CEO, Flextron

Akhil Jayaprakash
Founder & CEO, Pulse Energy

Vasudha Madhavan
Founder & CEO, Ostara Advisors

Seshadri Raghavan
Program Lead Sustainable Mobility, CEEW

Chaitanya Kanuri
Associate Director
E-Mobility, WRI

Sumedh Agarwal
Director, Smart & Resilient
Power & Mobility, AEEE

Shailesh Vickram Singh
Founder & CEO, GoMassive Earth Network (Moderator)
Key DISCUSSION HIGHLIGHTS
Subsidies should not be directed at CPOs or OEMs but instead at DISCOMs, as reliable electricity supply is one of the biggest bottlenecks in the expansion of EV charging infrastructure.
The presence of multiple charging standards in India undermines the very purpose of having a standardized framework, leading to inefficiencies in the market.
Public charging infrastructure should be developed based on actual utilization patterns. E.g., estimates suggested 50% of 3W would use public charging, many drivers in smaller cities charge at home, reducing public demand.
Consolidating charging station visibility across platforms and focusing on customer needs can catalyze adoption and drive equity into the EV charging ecosystem.
Urban areas require integrated solutions for last-mile connectivity and public transport hubs, while rural areas could benefit from fleet-focused charging stations, such as those for e-commerce and food delivery networks.
There is a need to focus on median and nominal usage scenarios rather than overbuilding infrastructure for peak demand, ensuring a sustainable and efficient rollout.


